Storage Profiles¶
Once you’ve defined data stores and enabled Atomix runtime integration on your application’s pods by injecting the runtime proxy, to use the data stores in your application you must define a StorageProfile.
apiVersion: atomix.io/v3beta3
kind: StorageProfile
metadata:
name: my-application
spec:
bindings:
- store:
name: my-memory-store
Injecting the StorageProfile¶
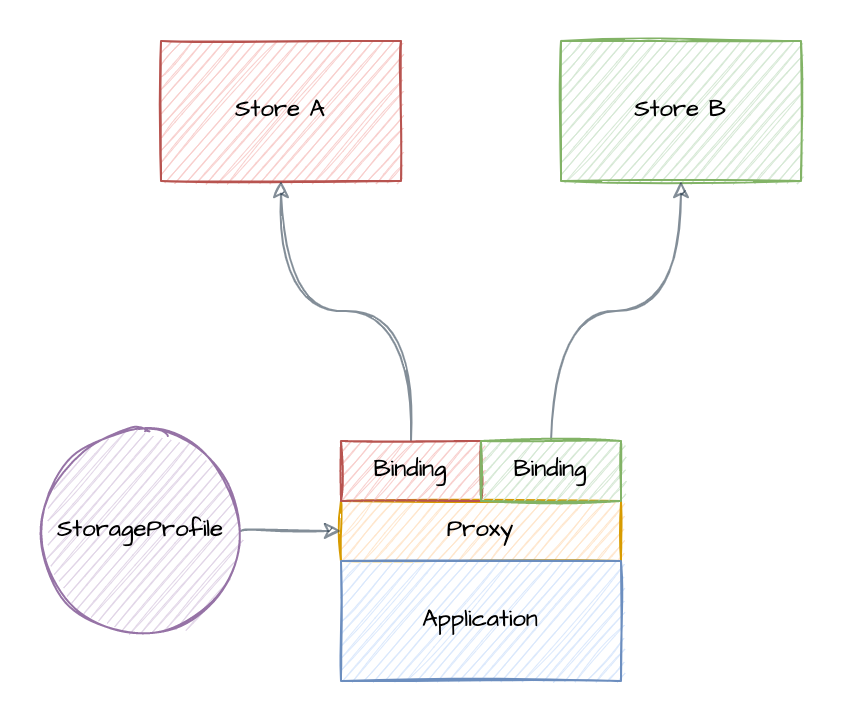
Storage profiles specify a set of bindings that define how the proxy routes primitives to stores. To associate your application with a StorageProfile, annotate the pods with the proxy.atomix.io/profile annotation:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: my-pod
namespace: default
annotations:
proxy.atomix.io/inject: "true"
proxy.atomix.io/profile: my-application
spec:
...
Configuring the proxy¶
Storage profiles can be used to configure the Atomix runtime proxy.
apiVersion: atomix.io/v3beta3
kind: StorageProfile
metadata:
name: my-application
spec:
proxy:
config:
server:
maxRecvMsgSize: 10Mi
maxSendMsgSize: 10Mi
maxConcurrentStreams: 1000
logging:
loggers:
root:
level: debug
bindings:
...
Routing primitives with tags¶
Applications can (and should) tag primitives with strings to aid in routing. Storage profiles can use tags to route primitives across multiple stores:
apiVersion: atomix.io/v3beta3
kind: StorageProfile
metadata:
name: my-application
spec:
bindings:
- store:
name: my-memory-store
tags:
- memory
- store:
name: my-consensus-store
tags:
- consensus
Configuring primitive proxies¶
bindings:
- store:
name: my-memory-store
tags:
- memory
rules:
- kind: Map
apiVersion: v1
config:
cache:
enabled: true